Migration scenarios
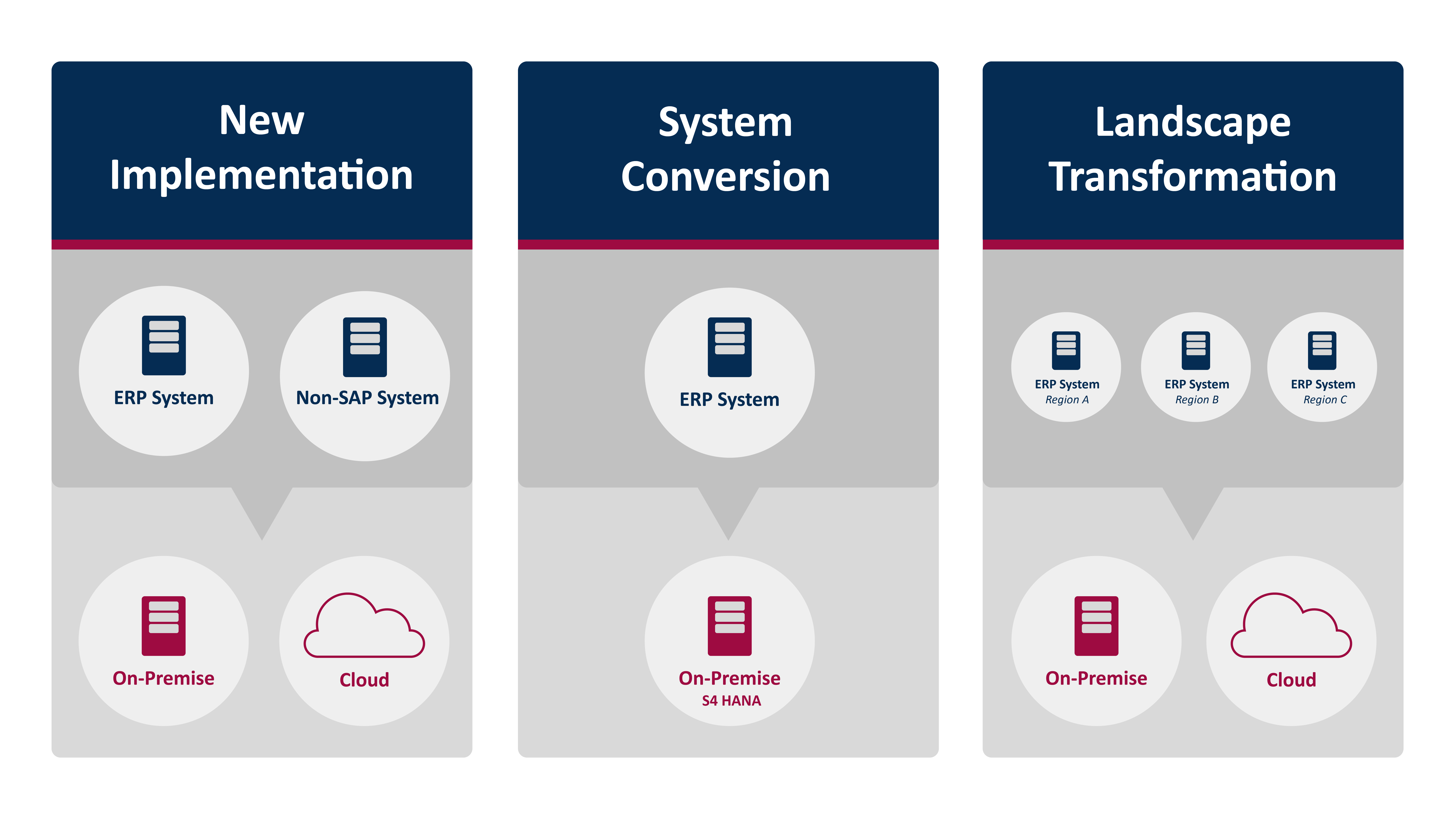
Scenario 1: New Implementation
This is a new implementation of SAP S/4HANA (green field): Customers who are migrating from a non-SAP legacy system or from an SAP ERP system and implementing a fresh system that requires an initial data load. In this scenario, the SAP S/4HANA system is implemented, and master and transactional data are migrated from the legacy system; thus, standard data migration tools and content must be used. You retire legacy customisations and work to streamline processes.
Scenario 2: System Conversion
This is a complete conversion of an existing SAP Business Suite system to SAP S/4HANA (lift & shift or brown field): customers who want to change their current SAP ERP system to SAP S/4HANA. This scenario is technically based on Software Update Manager (SUM) with Database Migration Option (DMO) in case the customer is not yet on SAP HANA as the underlying database.
Scenario 3: Landscape Transformation
This is a consolidation of current regional SAP systems into one global SAP S/4HANA system or a split out of different parts of a system: customers who want to consolidate their landscape or carve out selected entities (such as a company code) or processes into a single SAP S/4HANA system. Or it can be S/4HANA to S/4HANA (carve-out), which entails the cloning of the SAP application itself (including the technical repository and the configuration and customising of the system), and second, the migration of all (but only) the application data, which relates to the divested business.